TAPAS Project: Training of personalized and adapted affective social skills with virtual cultural agents
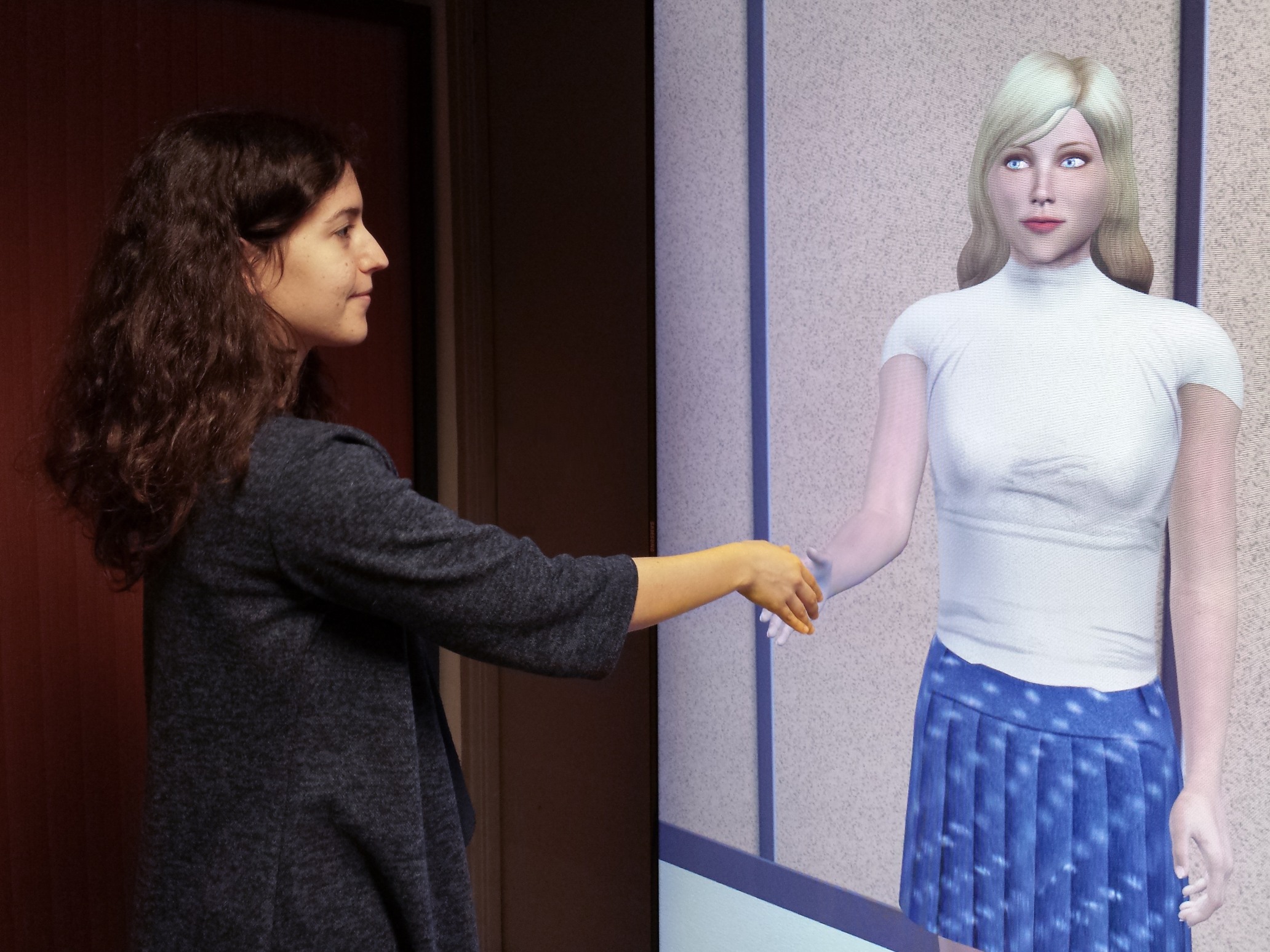
The proposal is targeted to develop tools and methods for Social Skill Training (SST) for a large variety of population. Social skills refer to managing verbal and nonverbal behaviors during an interaction with one or more persons. People facing difficulties interacting with others suffer from using appropriately their social behaviors and interpreting them in others. SST is used by therapists to train people to practice social interaction and overcome their social fear. It relies on role play as a means to put participants in a controlled social situation.
Context
Conventional SST is an established method that was originally developed to reduce anxiety and discomfort and to learn appropriate skills required during social interactions. SST effectively improves social skills for people with ASD. The basic SST training model follows five steps: instruction, modeling, role-playing, feedback, and homework. In addition, we will model Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) such as ‘Cognitive Reframing,’ which is a useful technique for understanding unhappy feelings and moods, and for challenging the sometimes-wrong “automatic beliefs” that can lie behind them. It requires to train users to manage their own multimodal behaviors as well as to pay attention and adapt to the behavior of their interactants in a social stress situation (eg. public speaking).
Objectives
TAPAS will develop tools and methods for SST to provide personalised training of social skills and help overcome social stress in such everyday situations involving (joint) presentation at school and at work. Our aim is to develop a platform allowing participants to role play social interactions. The targeted population is neurotypical individuals but also individuals with different scales of social pathologies including shyness, alexithymia and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). We will inspire the design of the platform from two mainstreams methods for social skills training: Conventional SST and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy.
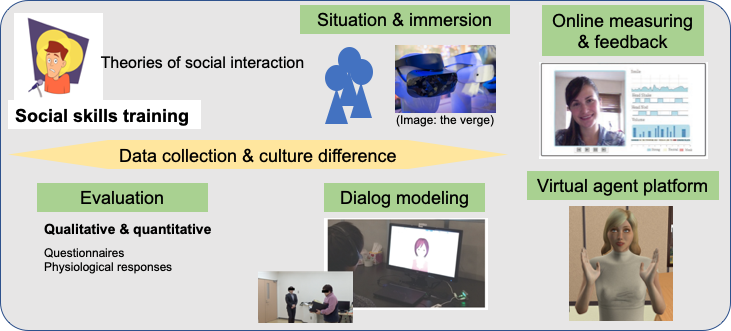
Results
We will design three relevant scenarios training different sets of social skills:
– train the user to work on a common task together with one or several virtual peer(s),
– train the user to maintain the attention and the engagement of a (small) virtual audience when presenting some material,
– train the user to jointly present with a virtual peer a joint work in front of a small virtual audience.
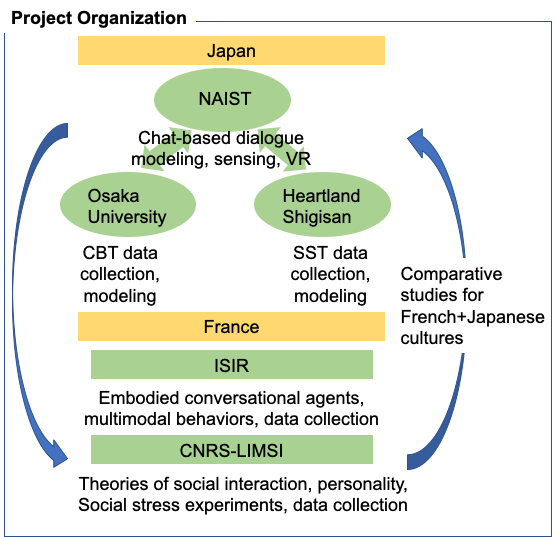
Partnerships and collaborations
– Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique (ISIR), France,
– Laboratoire d’Informatique pour la Mécanique et les Sciences de l’Ingénieur (LIMSI), CPU group, France,
– Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Data Science Center, Japan.